In today’s digital world, safeguarding sensitive information is more crucial than ever. Whether it’s protecting passwords, verifying data integrity, or securing digital transactions, hash functions play a fundamental role. This article delves into understanding Hash functions: the backbone of data security, exploring their purpose, how they work, and why they are indispensable in modern cybersecurity.
What Are Hash Functions?
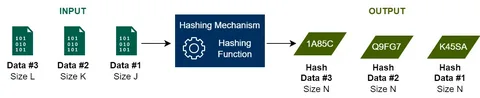
At their core, hash functions are mathematical algorithms that take an input (or “message”) and convert it into a fixed-size string of characters, which appears random. This output is known as the “hash value” or “digest.” The key feature of hash functions is that even a tiny change in the input produces a completely different hash, making it easy to detect any alterations.
How Hash Functions Enhance Data Security
The importance of understanding hash functions: the backbone of data security lies in their numerous applications:
- Password Protection: Instead of storing actual passwords, systems store their hashed versions. When a user logs in, the entered password is hashed and compared with the stored hash, ensuring the real password never needs to be saved or exposed.
- Data Integrity Verification: Hash functions can confirm that files or messages have not been tampered with during transmission. If the hash of the received data matches the original hash, the data is considered intact.
- Digital Signatures and Certificates: Hash functions are integral in generating digital signatures, which verify the authenticity and integrity of digital documents.
Characteristics of Secure Hash Functions
For hash functions to serve as the backbone of data security, they must possess several critical properties:
- Deterministic: The same input always results in the same hash output.
- Fast Computation: Hash values should be generated quickly to handle large volumes of data.
- Pre-image Resistance: It should be computationally infeasible to reverse-engineer the original input from its hash.
- Collision Resistance: Two different inputs should not produce the same hash output.
- Avalanche Effect: A small change in the input drastically changes the hash.
Popular Hash Functions in Use Today
Several hash algorithms have been developed over time, each designed to meet evolving security needs. Some widely used hash functions include:
- MD5: Once popular but now considered vulnerable due to collision attacks.
- SHA-1: More secure than MD5 but gradually being phased out in favor of stronger versions.
- SHA-256 and SHA-3: Current standards providing robust security for most applications.
Conclusion
Understanding hash functions: the backbone of data security is essential for anyone involved in digital security or data management. These functions form the foundation for many security protocols by ensuring data integrity, protecting sensitive information, and enabling secure communications. As cyber threats continue to evolve, the role of hash functions remains critical in safeguarding our digital lives.